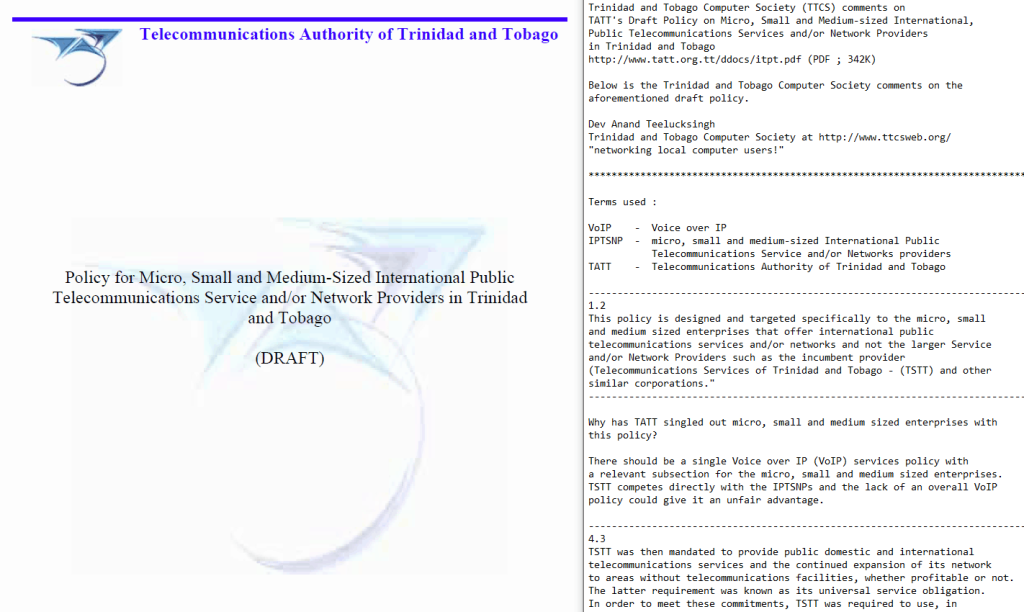
Following the Draft National Policy on Electronic Transactions (2004) and Draft National Policy on Electronic Transactions (2005), the Ministry of Public Administration and Information (MPAI) released the final Electronic Transactions Policy in January 2006.
- Download the National Policy on Electronic Transactions (PDF ; 41 pages ; size: 129K)
- Download the Explanatory Memorandum of the Electronic Transactions Policy (PDF ; 20 pages ; size: 64K)
The Policy will guide the Electronic Transactions Bill that will be introduced in Parliament in the future.